|
 |
 |
| RU |
|
Login
Newsletters
There is no newsletter category found. Information
|
Rohde & Schwarz improves signal integrity debugging with innovative jitter decomposition approach for its oscilloscopes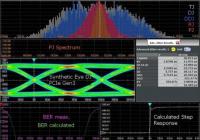 02/11/2020 Rohde & Schwarz has developed a novel and powerful method for analyzing the individual components of jitter, providing electronic circuit designers with previously unavailable in-depth knowledge invaluable for debugging high-speed signals. As data rates increase and voltage swings decrease, the jitter in digital interfaces becomes a significant percentage of the signaling interval, and potential source of failures. Increasingly, engineers require tools that accurately characterize the signal jitter including the break-down into its individual components. The new R&S RTO-/ RTP-K133 advanced jitter analysis option introduces an analytic approach to separating the individual components of jitter such as random jitter, and deterministic jitter components, such as data dependent and periodic jitter. This approach is based on a parametric signal model that fully characterizes the behavior of the transmission link under test. A core benefit of this Rohde & Schwarz method is that the jitter model includes the complete waveform characteristic of the signal under test, in contrast to conventional methods that reduce the data to a set of Time Interval Error measurements. The result is consistent measurement data even for relatively short signal sequences, plus previously unavailable information such as the step response, or a distinction between vertical and horizontal periodic jitter. Engineers benefit from in-depth details with jitter representations such as synthetic eye diagrams, histograms of all individual jitter components, spectral and peak views of periodic jitter, and the bathtub plot for estimating bit error rate. www.rohde-schwarz.com Company profile: Rohde & Schwarz Related Information:
Companies' news
KIPiS articles
|
Current issue
Search
|
|
|
| © "Test & Measuring Instruments and Systems" ("KIPiS"), 2000-2024 |